Brain Tumor: Causes and Treatment.
Have you or someone in your family been diagnosed with a brain tumor? You have a lot of doubts that need to be answered and assured that there are treatments for brain tumors. Speak to your neurosurgeon in Andhra Pradesh. Your doctor is your best guide in these times.
Brain tumors might compromise brain function if it grows large enough to push on nearby nerves, blood vessels, or tissue. Your recovery from the tumor largely depends on:
- The tumor’s type, grade, and location.
- The success of tumor removal surgery.
- Your age and overall health.
Dr. Mohana Rao Patibandla, the founder of Dr. Rao’s Hospital, is amongst the best neurosurgeons in Andhra Pradesh.
Dr. Rao’s Hospital is a state-of-the-art neurology hospital in Guntur, with an aim to give comprehensive treatment facilities to patients suffering from brain, spine, and nerve damage or abnormality.
If you or anyone in your family is looking for the best brain tumor treatment in Guntur, we have some of the best neurologists and neurosurgeons working with us.
To know more about brain tumor treatment, please continue reading this article.
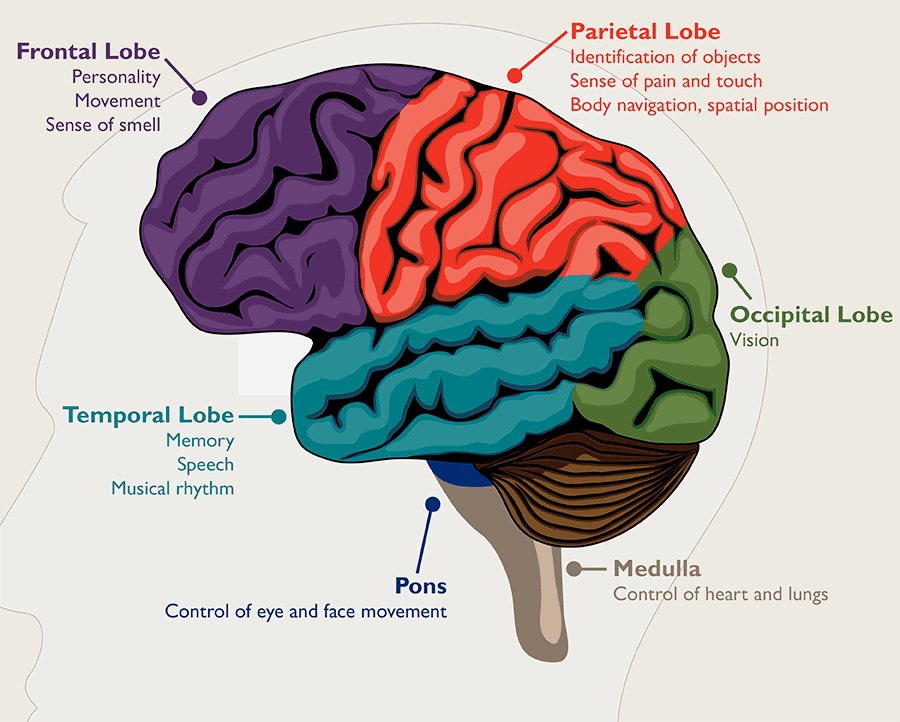
First, let’s know,
What is a brain tumor?
Cells that have grown abnormally in or around the brain is called a brain tumor.
Brain tumors can be either benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous). Some tumors develop swiftly, while others grow slowly.
Only approximately a third of all brain tumors are malignant. Even if they are benign, brain tumors can affect brain function by impinging on surrounding nerves, blood vessels, and tissue.
Primary tumors are those that form in the brain.
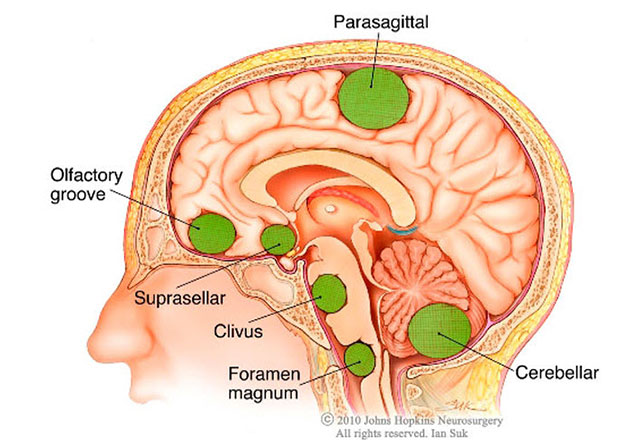
Secondary tumors or metastatic tumors have moved to the brain growing from another section of the body.
Here, we will get some information on primary tumors. Primary brain and spinal cord tumors come in a variety of shapes and sizes.
Types of Primary Brain Tumors:
Tumors of the brain and central nervous system are classified by their location and the type of cells they affect.
Benign brain tumors:
Vestibular schwannomas, also named acoustic neuromas, is a tumor that develops on the vestibular nerve (the nerve that leads from the inner ear to the brain).
Pineocytoma: Pineocytoma is a slowly progressing tumor of the pineal gland, situated in the deep brain, and secretes melatonin hormone.
Gangliocytoma: These tumors develop in neurons (nerve cells) and affect the central nervous system.
Meningioma: A tumor in the meningeal layer that protects the brain and spinal cord. They are mostly non-cancerous.
Pituitary adenoma: These tumors develop in the pituitary gland near the base of the brain.
Chordoma: Chordomas are slow-growing tumors that usually start at the base of the skull or the bottom of the spine. They’re mostly harmless (not cancerous).
Malignant brain tumors:
Glioma: Glioma is a type of tumor that develops in the glial cells surrounding and aid nerve cells. Gliomas are classified as follows:
Astrocytomas are tumors that develop in the glial cells known as astrocytes.
Glioblastoma: Glioblastomas are astrocytomas that grow aggressively.
Oligodendroglioma: These rare malignancies start in myelin-producing cells (a layer of insulation around nerves in the brain).
Medulloblastomas are rapidly growing tumors that originate at the base of the skull. They mostly prevail in children.

What causes brain tumors?
A variety of factors causes a brain tumor.
- Unusual cell propagation is caused by a genetic mutation.
- Radiation from X-rays.
- Chemicals in the environment.
- Family history.
What signs and symptoms do you have if you have a brain tumor?
A brain or central nervous system tumor can cause no symptoms in some persons. Doctors may detect cancer while treating another problem in some situations.
A brain tumor may create symptoms when it grows and presses on nearby nerves or blood vessels. The location, nature, and size of a brain tumor and the affected portion of the brain influence the signs and symptoms. They may include the following:
- Headaches that are persistent or severe, or that begin first in the morning or disappear after vomiting.
- Changes in behavior or personality.
- Confusion.
- Problems with balance and coordination.
- Trouble concentrating.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Tingling, numbness, or weakness in one side or section of the body or face.
- Vision, hearing, or speech difficulties.
- Seizures.
- In ordinary sleepiness
- Thinking, memory, speaking, and understanding language problems
Diagnosis of Brain Tumour:
Doctors use several tests to confirm the presence of a brain tumor. These tests include the following:
Physical examination and medical history: Your doctor will do a general physical examination to search for signs of sickness. Your doctor will also inquire about your past and present surgeries and medical treatments and family history of diseases.
Blood test: To see if there are any tumor markers.
Biopsy: A tissue sample is taken and sent for testing.
PET scans, CT, MRI, and SPECT are imaging techniques that assist doctors in finding tumors and deciding whether they are malignant or benign.
Spinal tap for the presence of a malignant tumor in the central nervous system.
A tumor is graded 1-4 based on how fast it is growing and likely to spread.
Treatment option for brain tumor:
The location, size, and kind of tumor determine the course of treatment. To treat a tumor, most neurosurgeons in Hyderabad frequently utilize a mix of medicines, surgeries, and radiation.
The surgeon decides the approach of the surgery to limit harm to functional parts of the brain.
They work very cautiously, sometimes performing surgery while the patient is conscious.
Sometimes, the surgeons have to perform a craniotomy, where they have to surgically cut out a fragment of the skull to reach the tumor.
Types of Craniotomy:
- Extended Bifrontal Craniotomy
- Retro-Sigmoid “Keyhole” Craniotomy
- Translabyrinthine Craniotomy
- Minimally Invasive Supra-Orbital “Eyebrow” Craniotomy
- Orbitozygomatic Craniotomy
Other Treatment Methods
Radiation:
High dosages of X-rays are used to kill brain tumor cells or reduce the tumor. Before surgery, some people receive radiation to reduce a brain tumor so that the surgeon has to remove less tissue.
Chemotherapy:
Anti-cancer medications destroy cancer cells in the brain and throughout the body during chemotherapy. Chemotherapy can be injected into a vein or taken orally. Sometimes, doctors will use chemotherapy before surgery to shrink the tumor. Following surgery, your doctor may recommend chemotherapy to eliminate any cancer cells that remain or to prevent tumor cells from developing.
Immunotherapy:
Immunotherapy, often known as biological therapy, is a cancer treatment that uses your body’s own immune system to fight the disease. The primary goal of the treatment is to activate the immune system.
Targeted therapy:
Drugs that target specific traits in cancer cells without hurting healthy cells are known as targeted treatments. If you are having problems with the adverse effects of chemotherapy, such as exhaustion and nausea, your doctor may offer targeted therapy.
Laser thermal ablation
Laser thermal ablation is a treatment that kills tumor cells with lasers.
Active follow-ups. A doctor uses regular tests to keep an eye on the tumor for symptoms of growth.
How may a brain tumor be prevented?
A brain tumor is unavoidable. Avoiding smoking and excessive radiation exposure can help you prevent having a brain tumor.
What is the prognosis for those who have a brain tumor?
Different people and brain tumors have different outcomes. The type, grade, and location of the tumor; effective removal of the entire tumor; and your age and overall health are all factors that can affect your prognosis.
In many patients, the surgeon can successfully treat a brain tumor.
Brain tumors can come back in some persons following therapy. To keep the tumor from developing or spreading, these people may need to continue treatments such as chemotherapy or radiation. Following brain tumor therapy, you should see your doctor regularly.


